Do you feel tired all the time? You may be shocked to hear that it is more than just a lack of energy. Dive into the world of mononucleosis. You need to understand why this common illness could be causing your chronic fatigue. Do not let tiredness keep you down. Today, we’ll look at the hidden truths about mononucleosis.
Mononucleosis is also called mono for short. It is a viral infection that can make you feel extremely exhausted and sick. It is most usually caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. But other viruses can produce similar symptoms. Mononucleosis is very dangerous. It spreads through sweat. Mononucleosis can be spread by kissing an infected person or exchanging items such as tools, glasses, or cups with them. Most people are exposed to the virus as kids or teens, but they may not become ill straight away. As a result, the virus remains in their body and can come back later in life, but this is rare. That’s why, the ER of Watauga ensures that you can receive the best recovery against these serious complications.
Mononucleosis usually begins with flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and swollen glands. It may cause severe fatigue that lasts weeks or even months. While the majority of cases of mononucleosis are minor. Some people may have serious problems, especially if they have weaker immune systems. In this blog, we will give you a guide about mononucleosis and also about its causes, symptoms, signs, and how you can cure mononucleosis.
WHAT IS MONONUCLEOSIS?

Infectious mononucleosis typically happens by the Epstein-Barr virus. However, it can sometimes be caused by the cytomegalovirus. It is easily transmitted from person to person via sweat, making it dangerous. It can spread through activities such as sharing drinks, straws, and toothbrushes. Mononucleosis can affect anyone at any age. However, it is more common among high school and college students. Once diseased, the virus may become latent in the body and reactivate when the immune system is weak. Luckily, most people who have had mononucleosis do not develop it again.
HOW DO YOU GET MONONUCLEOSIS?
Epstein-Barr virus causes infectious mononucleosis. You can catch EBV by coming into touch with saliva from someone who is infected. Many people are given EBV during their youth, often without ever recognizing it. Teenagers and young adults who have not been impacted usually become infected after coming into contact with spreading saliva. Once exposed to EBV remains latent in the body for the rest of one’s life, this condition is known as “transmissible latency”. People with EBV can knowingly transfer the virus through saliva wiping. This transmission may also occur by other physiological fluids, such as cells or vaginal discharge.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF MONONUCLEOSIS?
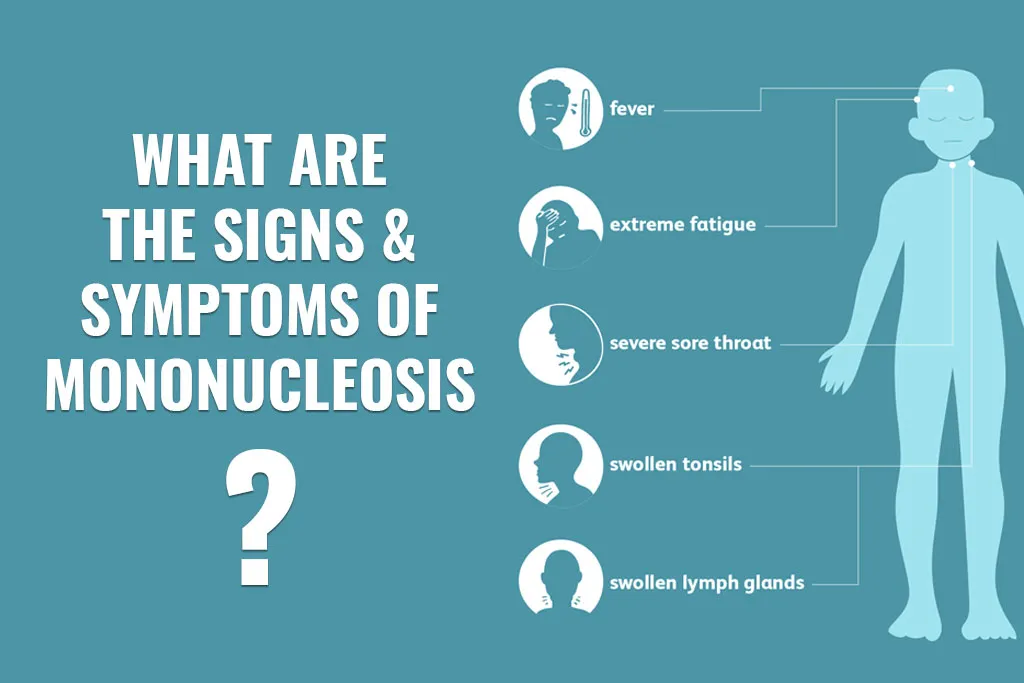
The virus has a waiting period of four to six weeks, though this can be shorter in small children. The incubation period is the amount of time it takes for you to experience symptoms after being exposed to the virus. Fever and sore throat are common signs and symptoms that often resolve within a few weeks. But drowsiness enlarged lymph vessels, and a swollen liver may linger several weeks longer.
Symptoms of mononucleosis may include
- Tiredness
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Swollen lymph vessels
- Headache
- Discomfort in the muscles and rash
- Swollen liver
- Loss of hunger
CHILDREN AND TEENAGERS
Mononucleosis symptoms in children and teenagers may differ. They tend to have fever, sore throat, larger lymph nodes, and tiredness. Children might experience abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. While, teenagers may experience additional symptoms such as headaches, muscle aches, and loss of desire. These symptoms might make it difficult for children and teenagers to take part in their normal activities. Parents need to carefully track their child’s symptoms. They can seek medical treatment if they believe in mononucleosis, especially if the symptoms improve or continue.
YOUNGER KIDS
Mononucleosis symptoms in young children can look similar to those in younger children and teenagers. Although, they may be more difficult to identify. They may experience a fever, sore throat, and swollen glands in their neck. Younger children may appear more picky than usual. They may not want to eat or drink as much. Sometimes they won’t be able to tell you what’s wrong. So, pay attention to any changes in their behavior or mood. If you detect any of these symptoms in your young child, contact a doctor for more testing and guidance.
OTHER ADULTS
Other adult’s mononucleosis symptoms may differ greatly. Although, they tend to involve weariness, sore throat, swollen glands, and fever. Some people may also have muscle aches, headaches, and a loss of taste. These symptoms can make it difficult to carry out regular activities, so rest and take care of yourself if you suspect you have mono. While most cases of mono cure on their own within a few weeks. If your symptoms are severe or ongoing, you should contact a doctor for a correct diagnosis and to explore treatment options.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF MONONUCLEOSIS?
Mononucleosis is mostly caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, which spreads by saliva. Kissing, sharing a meal or drink, and using objects that have previously been used by an infected person can all spread the infection. A lot of people have been given EBV and produced antibodies that make them immune to mononucleosis. Mononucleosis can occur at any age. But it is more common in people aged 15 to 25, likely due to more personal contact with others. After the virus enters the body, symptoms can appear 4 to 10 weeks later.
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT OF MONONUCLEOSIS?
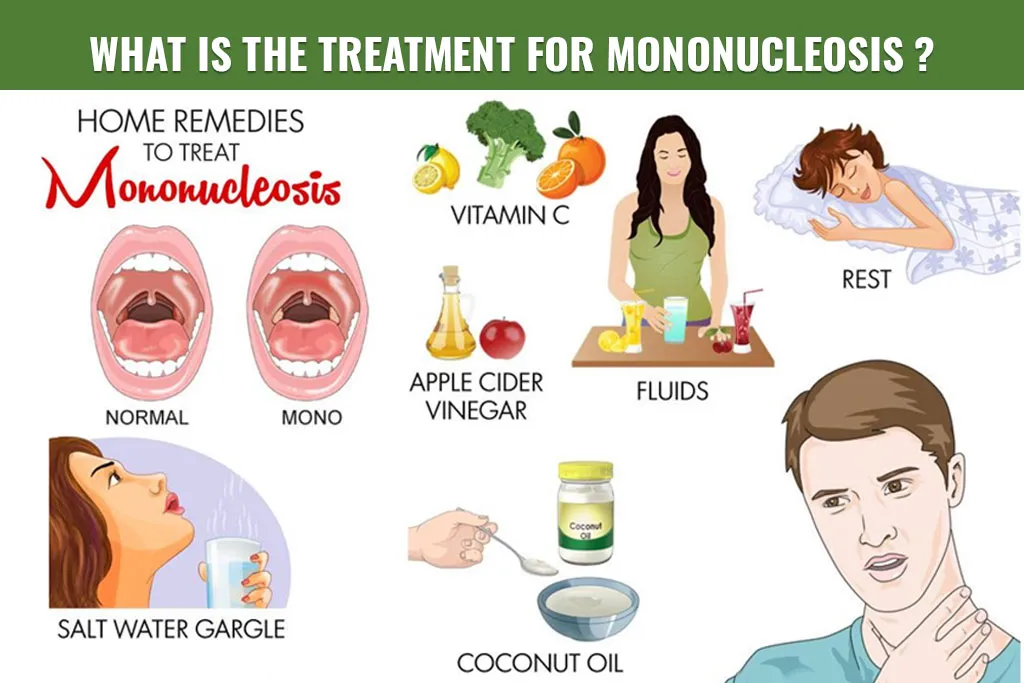
There is no specific treatment for infectious mononucleosis. But your doctor may prescribe steroids to help with throat and tonsil swelling. In most cases, the symptoms heal on their own after a month or two. The best treatment is getting plenty of rest, drinking lots of liquids, and eating healthy. Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to treat sore throats, muscle aches, and fevers. Don’t give aspirin. Giving aspirin can cause Reye syndrome, a severe sickness. If the tonsils or lymph nodes in the neck are severely swollen and causing difficulty breathing, the doctor may prescribe steroid medication. People with mononucleosis should avoid engaging in contact sports and intense physical activity until their doctor advises it is safe. Even fun wrestling at home might be harmful to an enlarged liver. For one month following recovery, avoid hard lifting and rough or energetic play.
WHAT IS THE TEST FOR MONONUCLEOSIS?

Mononucleosis is a viral illness caused by a virus. The Epstein-Barr virus is the most common cause of mononucleosis. But other viruses can also cause the illness. There are three types of mononucleosis tests
MONONUCLEOSIS SPOT TEST
A mononucleosis spot test is a blood test to identify if you have the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes infectious mononucleosis. If you are experiencing mononucleosis symptoms, your doctor may refer this test. Mononucleosis is a viral disease that targets certain blood cells, creating flu-like symptoms.
The Mononucleosis spot test detects heterophile antibodies that the immune system produces in response to EBV infection. These antibodies can react with various types of cells, such as horse red blood cells. A comparable test, the Paul-Bunnell test, reveals a response with sheep red blood cells. EBV produces infectious mononucleosis, which is a self-limited condition.
EBV ANTI-BODY TEST
The Epstein-Barr virus belongs to the herpesvirus family. It’s one of the most frequent viruses that infect humans worldwide. In general, the virus causes no symptoms in youngsters. It produces an infection known as infectious mononucleosis, in around 35 to 50 percent of young people and adults. EBV spreads mostly by saliva. The disease often spreads through blood or other parts of the body. The EBV test is often referred to as EBV antibodies. It is a blood test designed to detect EBV infection. The test identifies the presence of antibodies. Antibodies are proteins produced by your immune system in reaction to a dangerous material known as an antigen. More specifically, the EBV test detects antibodies to EBV proteins. The test can detect both current and historical infections.
RAPID MONONUCLEOSIS TEST
The rapid mononucleosis test is used to diagnose a recent mono-infection. The EBV antibody test can help you identify if you’ve ever been infected with the virus and how recent the infection was. EBV antibody testing is typically performed when you have symptoms of infectious mononucleosis and a fast mononucleosis test is negative. When a person takes medication that causes immune system difficulties, EBV antibody testing may also be performed to detect antibodies to EBV
HOW LONG DOES MONONUCLEOSIS LAST?
The Epstein-Barr virus is the most common cause of mono. Symptoms of mononucleosis might occur four to six weeks after infection. The period between infection and the start of symptoms is known as the incubation period. Even if you feel good, you could still spread the illness to others.
Mononucleosis occurs in three stages, which are discussed below
1st STAGE OF MONONUCLEOSIS
The first stage of mononucleosis is known as the prodrome stage. It normally lasts three or five days. It causes low energy, discomfort, lack of weight, and sore throat. Mononucleosis can sometimes occur without any symptoms. Children under the age of ten may experience very little or no symptoms at all.
2nd STAGE OF MONONUCLEOSIS
The second stage of mononucleosis is known as the acute stage. Its symptoms may become worse. These acute symptoms are generally referred to as classical mononucleosis symptoms. Usually, they remain 2 to 4 weeks. It’s important to remember that not everyone will experience every symptom of mononucleosis. They may occur at various points throughout the infection.
3rd STAGE OF MONONUCLEOSIS
The final stage of mononucleosis is known as the convalescent stage. This is when you recover from the infection, which can take three to six months. Symptoms in this stage of mononucleosis gradually improve. But tiredness might last for weeks or even months. It’s critical to rest and relax at this time to aid in recovery.
HOW LONG IS MONONUCLEOSIS CONTAGIOUS?
It is still unclear how long mono infections can be contagious after symptoms clear. Most persons with mononucleosis are contagious for around 6 months. In some cases, it could remain contagious for up to 18 months. During this time, anyone with mononucleosis can infect others. Mononucleosis is a more commonly used source among teenagers and young adults, particularly college students. EBV may have infected approximately 95% of persons by the time they reach maturity. People who use antiviral medication to treat mononucleosis may recover more quickly, but the proof is not clear. More research is needed to determine whether this medication impacts how contagious the virus is.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO GET MONONUCLEOSIS TWICE?
Once infected, the Epstein-Barr virus remains in your body, usually inactive. This shows that it does not create any symptoms or harm. In general, your immune system keeps the infection in check. However, if your immune system declines, the virus may reactivate and cause symptoms again. This does not imply that you have been infected with a new virus. It simply indicates that the same virus has become active again. While this reactivation is uncommon, it might make you feel sick.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING A MONONUCLEOSIS TEST?

If you have mononucleosis symptoms, your doctor would suggest you have mononucleosis tests. According to the doctor’s guidelines, you must submit a blood sample from your fingertip or a vein. These tests will not take very long to complete. Both tests are quick. It normally takes around five minutes.
FOR A FINGER-TIP BLOOD TEST
During a finger-tip blood test, a healthcare expert would lightly prick your finger, generally on the middle or ring finger. After wiping away the first drop of blood, they will place a small bit in a tube. When the needle makes contact with your skin, you may feel a tiny pinch.
FOR A BLOOD TEST FROM A VEIN
During a blood test from a vein, a healthcare provider will draw blood from a vein in your arm with a little needle. After injecting the needle, they will draw a small amount of blood into a test tube or vial. When you insert or remove the needle, you may feel a minor pain.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, mononucleosis is a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. It spreads through contact with infectious saliva. While painful, mononucleosis usually goes away on its own with no residual effects. Symptoms like as tiredness, fever, and sore throat may persist for several weeks. Most people only get mononucleosis once, as the virus remains silent in the body after recovery. In some situations, the virus may come back, although usually without causing any obvious symptoms.
Good hygiene is essential for preventing the virus from spreading, particularly among adolescents and young adults. If you suspect mononucleosis, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. In this case, the ER of Watauga can provide you with the best treatment against this disease. You can rely on us. Contact us at any time. We are just a step away from you.
FAQ
Can cats get mononucleosis?
No, cats can’t get mononucleosis. The Epstein-Barr virus causes mononucleosis, which is specific to humans. While cats can develop their viruses and diseases, mononucleosis is not one of them. However, keeping your cat healthy requires regular checkups and vaccines.
How much is the death rate due to mononucleosis?
The rate of death from mononucleosis is extremely low, with the majority of cases resolving on their own without problems. However, in rare cases, serious effects such as organ failure or an enlarged liver might occur, resulting in death. If you have serious symptoms or effects from mononucleosis, you should seek medical attention immediately to receive proper treatment and assistance.
Can mononucleosis kill you?
Mononucleosis is usually harmful. Although, it has serious effects such as organ failure or a burst liver can be life-threatening. If you have serious symptoms or implications contact your doctor right away. Early intervention can prevent serious consequences.
How many times can you get mononucleosis?
Most people only have mononucleosis once throughout their lives because once infected, their bodies develop immunity to the virus. In some cases, mononucleosis can reactivate, especially in patients with weaker immune systems. So, while unique, it is possible to get mononucleosis more than once.
Does mononucleosis affect the liver?
Yes, Mononucleosis can harm the liver. The Epstein-Barr virus that causes mono can cause liver damage, leading to symptoms such as a condition known as stomach pain, and liver size.
What is the differential diagnosis for mononucleosis?
Mononucleosis differential diagnosis includes various disorders that have similar symptoms, such as viral tonsillitis, the flu, and CMV infection. A complete assessment including a physical examination and laboratory tests. It is required to distinguish between these illnesses and confirm a mononucleosis diagnosis.